본 글에선 스택과 큐에 대해 알고 있다는 가정하에 설명합니다.
DFS와 BFS는그래프에서 탐색을 하기 위한 알고리즘입니다.
그래프는 아래와 같이 노드와 간선으로 이루어진 구조를 말합니다.
잘 아실 이진트리도 이에 해당합니다.

긴말 없이 DFS부터 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
Depth First Search
DFS는 자료구조 stack을 이용해 구현됩니다.
DFS의 작동 과정을 말로 먼저 알아보면
- 시작 노드를 스택에 삽입하고 방문처리한다.
- 스택의 최상단 노드에 방문하지 않은 인접 노드를 스택에 삽입하고 방문처리한다.(여러 개일 경우 통상적으로 가장 작은 노드부터 삽입한다.)
- 방문하지 않은 인접 노드가없을 경우 최상단 노드를 꺼낸다.
- 방문하지 않은 노드가 없을 때 까지 과정 2,3번을 반복한다.
탐색의 시간 복잡도는 O(N)입니다.
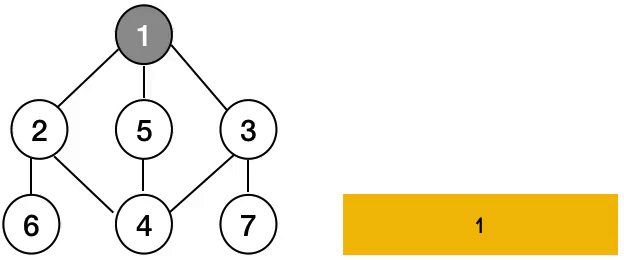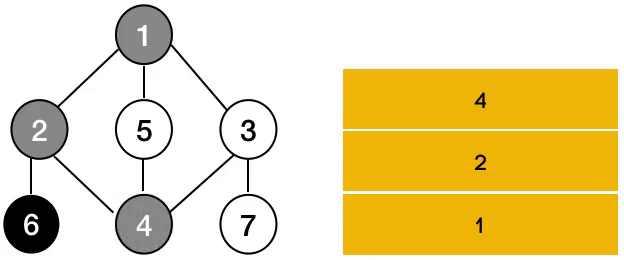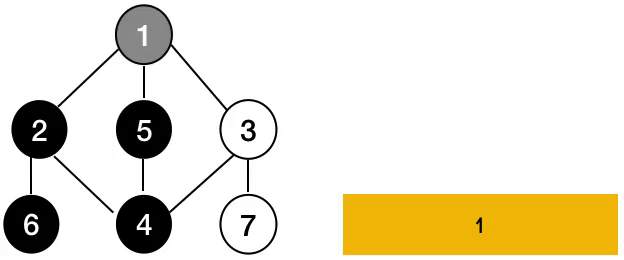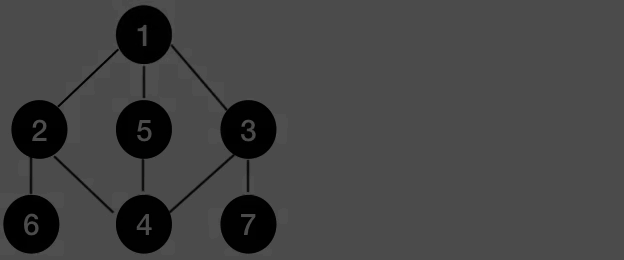
사진으로 알아보면 위와 같습니다.
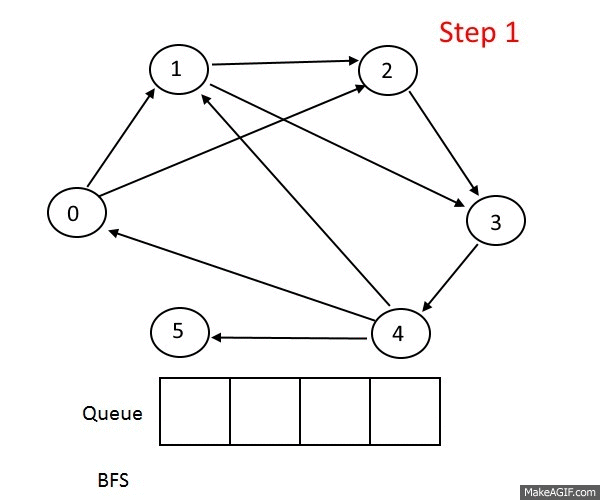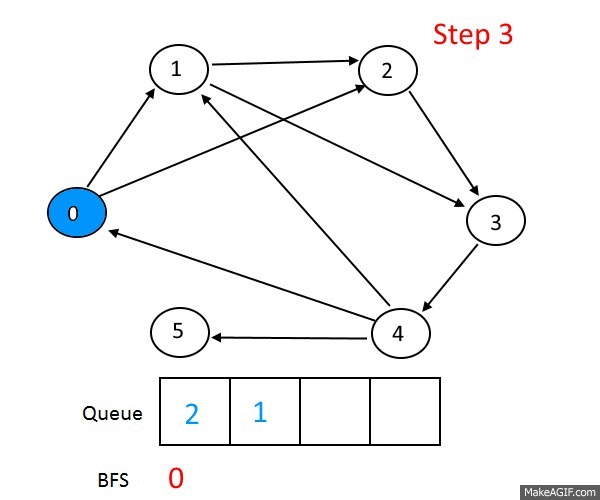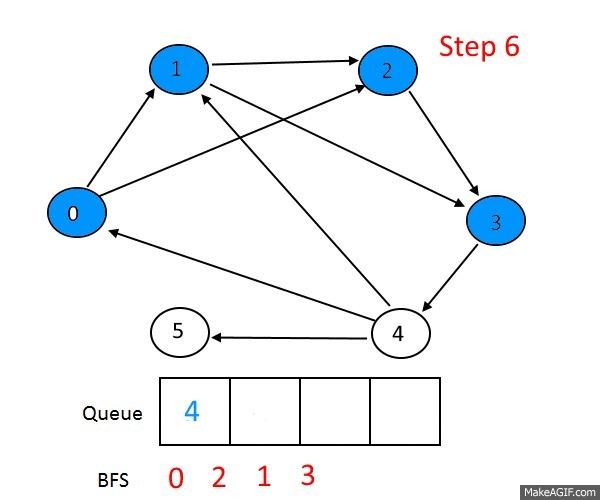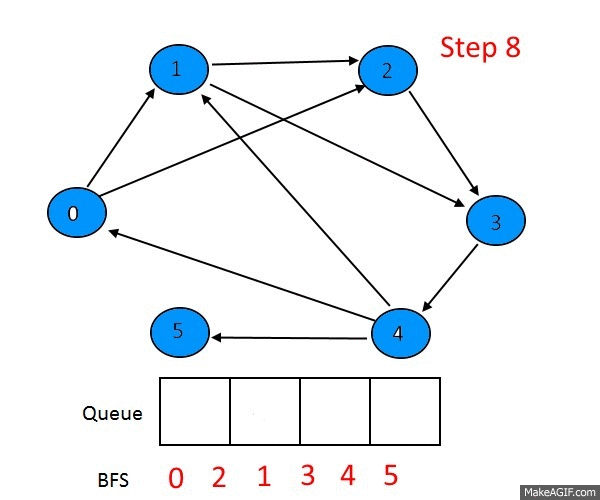
Breath First Search
BFS는 자료구조 queue를 이용해 구현됩니다.
BFS의 작동 과정을 말로먼저 알아보면
- 시작 노드를 큐에 삽입하고 방문처리한다.
- 큐에서 노드를 꺼내고 방문하지 않은 인접노드를 큐에 삽입한다.(여러 개일 경우 통상적으로 노드 크기로 오름차순 하여 삽입한다.)
- 방문하지 않은 인접노드가 없을 경우 무시한다.
- 방문하지 않은 노드가 없을 때 까지 과정 2,3번을 반복한다.
탐색의 시간 복잡도는 DFS와 똑같이 O(N)이지만 일반적으로 실제 수행 시간은 DFS보다 좋은 편입니다.
그럼 문제를 같이 하나 풀어보죠
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/60063
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
from collections import deque
def solution(board):
n = len(board)
q = deque([[[1,1],[1,2],0,False]]) # pos(left,up), pos(right,down), cost, is_vertical
h_visited = [[False] * (n+2) for _ in range(n+2)]
v_visited = [[False] * (n+2) for _ in range(n+2)]
board = [[1] * (n+2)] + [[1]+b+[1] for b in board] + [[1] * (n+2)]
while q:
state = q.popleft()
if state[3]:
if v_visited[state[0][0]][state[0][1]] and v_visited[state[1][0]][state[1][1]]:
continue
else:
if h_visited[state[0][0]][state[0][1]] and h_visited[state[1][0]][state[1][1]]:
continue
print(state)
if [n,n] in state: return state[2]
if not state[3]:
h_visited[state[0][0]][state[0][1]] = True
h_visited[state[1][0]][state[1][1]] = True
# left
if board[state[0][0]][state[0][1]-1] == 0 and not h_visited[state[0][0]][state[0][1]-1]:
q.append([[state[0][0], state[0][1]-1],state[0], state[2]+1, False])
# right
if board[state[1][0]][state[1][1]+1] == 0 and not h_visited[state[1][0]][state[1][1]+1]:
q.append([state[1], [state[1][0],state[1][1]+1], state[2]+1, False])
# up
if board[state[0][0]-1][state[0][1]] == 0 and board[state[1][0]-1][state[1][1]] == 0 and (not h_visited[state[0][0]-1][state[0][1]] or not h_visited[state[1][0]-1][state[1][1]]):
q.append([[state[0][0]-1,state[0][1]], [state[1][0]-1,state[1][1]], state[2]+1, False])
# down
if board[state[0][0]+1][state[0][1]] == 0 and board[state[1][0]+1][state[1][1]] == 0 and (not h_visited[state[0][0]+1][state[0][1]] or not h_visited[state[1][0]+1][state[1][1]]):
q.append([[state[0][0]+1,state[0][1]], [state[1][0]+1,state[1][1]], state[2]+1, False])
# right to up
if board[state[0][0]-1][state[0][1]] == 0 and board[state[1][0]-1][state[1][1]] == 0 and not v_visited[state[0][0]-1][state[0][1]] and not v_visited[state[1][0]-1][state[1][1]]:
q.append([[state[0][0]-1,state[0][1]], state[0], state[2]+1, True])
# right to down
if board[state[0][0]+1][state[0][1]] == 0 and board[state[1][0]+1][state[1][1]] == 0 and not v_visited[state[0][0]+1][state[0][1]] and not v_visited[state[1][0]+1][state[1][1]]:
q.append([state[0], [state[0][0]+1,state[0][1]], state[2]+1, True])
# left to up
if board[state[0][0]-1][state[0][1]] == 0 and board[state[1][0]-1][state[1][1]] == 0 and not v_visited[state[0][0]-1][state[0][1]] and not v_visited[state[1][0]-1][state[1][1]]:
q.append([[state[1][0]-1,state[1][1]], state[1], state[2]+1, True])
# left to down
if board[state[0][0]+1][state[0][1]] == 0 and board[state[1][0]+1][state[1][1]] == 0 and not v_visited[state[0][0]+1][state[0][1]] and not v_visited[state[1][0]+1][state[1][1]]:
q.append([state[1], [state[1][0]+1,state[1][1]], state[2]+1, True])
if state[3]:
v_visited[state[0][0]][state[0][1]] = True
v_visited[state[1][0]][state[1][1]] = True
# left
if board[state[0][0]][state[0][1]-1] == 0 and board[state[1][0]][state[1][1]-1] == 0 and (not v_visited[state[0][0]][state[0][1]-1] or not v_visited[state[1][0]][state[1][1]-1]):
q.append([[state[0][0],state[0][1]-1], [state[1][0],state[1][1]-1], state[2]+1, True])
# right
if board[state[0][0]][state[0][1]+1] == 0 and board[state[1][0]][state[1][1]+1] == 0 and (not v_visited[state[0][0]][state[0][1]+1] or not v_visited[state[1][0]][state[1][1]+1]):
q.append([[state[0][0],state[0][1]+1], [state[1][0],state[1][1]+1], state[2]+1, True])
# up
if board[state[0][0]-1][state[0][1]] == 0 and not v_visited[state[0][0]-1][state[0][1]]:
q.append([[state[0][0]-1, state[0][1]],state[0], state[2]+1, True])
# down
if board[state[1][0]+1][state[1][1]] == 0 and not v_visited[state[1][0]+1][state[1][1]]:
q.append([state[1], [state[1][0]+1,state[1][1]], state[2]+1, True])
# down to left
if board[state[0][0]][state[0][1]-1] == 0 and board[state[1][0]][state[1][1]-1] == 0 and not h_visited[state[0][0]][state[0][1]-1] and not h_visited[state[1][0]][state[1][1]-1]:
q.append([[state[0][0],state[0][1]-1], state[0], state[2]+1, False])
# down to right
if board[state[0][0]][state[0][1]+1] == 0 and board[state[1][0]][state[1][1]+1] == 0 and not h_visited[state[0][0]][state[0][1]+1] and not h_visited[state[1][0]][state[1][1]+1]:
q.append([state[0], [state[0][0],state[0][1]+1], state[2]+1, False])
# up to left
if board[state[0][0]][state[0][1]-1] == 0 and board[state[1][0]][state[1][1]-1] == 0 and not h_visited[state[0][0]][state[0][1]-1] and not h_visited[state[1][0]][state[1][1]-1]:
q.append([[state[1][0],state[1][1]-1], state[1], state[2]+1, False])
# up to right
if board[state[0][0]][state[0][1]+1] == 0 and board[state[1][0]][state[1][1]+1] == 0 and not h_visited[state[0][0]][state[0][1]+1] and not h_visited[state[1][0]][state[1][1]+1]:
q.append([state[1], [state[1][0],state[1][1]+1], state[2]+1, False])간단히 BFS구현만으로 풀 수 있습니다.
while문에서 제일 처음으로 나오는 if문은 시간 초과를 해결하기 위한 부분입니다.
'algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 그리디 알고리즘 (0) | 2023.01.11 |
|---|---|
| Heap sort 힙정렬 (0) | 2023.01.07 |